How To Calculate Resultant Amplitude
Furthermore in this topic you will learn about the amplitude amplitude formula formulas derivation and solved example. Amplitude square root FFT x FFT FFTimag x FFTimag And next to Amplitude in the results spreadsheet is Frequency Index.

Principle Of Superposition Of Wave Resultant Intensity Superposition Superposition Of Waves Youtube
The amplitude of the resultant wave is Ar3A A r 3 A and its intensity is IrcA2r3cA23I0 I r c A r 2 3 c A 2 3 I 0.
How to calculate resultant amplitude. Methods for calculating a Resultant Vector. Amplitude is something that relates to the maximum displacement of the waves. You must first add the amplitudes and then square them to find the intensity.
Next you need to write the sum of waves in exactly the same form by using the identity cosa b cosacosb sinasinb. The counterclockwise angle that R makes with the positive x-axis which in our case is 180 ie. It is easier at first to assume that the amplitudes of the superposing waves are the same A.
Each wave is a periodic disturbance. Try the following formula for the resultant amplitude. To express the direction of R we need to calculate the direction angle ie.
Note that y1 and y4 are out of phase and interfere destructively. There are a two different ways to calculate the resultant vector. As we know Intensity Amplitude 2 I ka.
The resultant amplitude of two interfering waves is equal to the sum of those two waves displacements at the same location as the resultant waves amplitude. Amplitude is the maximum displacement of the wave. The process that we used in this case and in the previous one to find the resultant force when the forces are not parallel can also be used when all the forces are parallel.
Nickzom Calculator solves for the resultant of the two vectors and shows you the formula workings and answer. Find the amplitude of the resultant wave produced due to interference of two waves given as y 1 A 1 sint y 2 A 2 sin t Advertisement Remove all ads. The resultant vector is the vector that results from adding two or more vectors together.
Click hereto get an answer to your question The resultant amplitude when two waves of same frequency but with amplitudes a1 and a2 superimpose with a phase difference of pi2 will be. Every time we add 6 dB actually the amplitude of the signal is doubled. Amplitude of sound particle velocity v or particle velocity amplitude amplitude of pressure gradient p or pressure gradient amplitude.
Note if you are opening the csv file using excel make sure to increase the. Start with two waves of equal amplitude A equal frequency w expressed in radians w 2f but with a phase difference x1 Acoswt x2 Acoswt . Then as the intensity is proportional to the amplitude squared the total intensity from the two sources individually is.
I ka and I kA k is a proportionality constant Resultant Intensity I I I 2II cos. Besides after completing the topic you will be able to understand amplitude. This is how the amplitude is calculated.
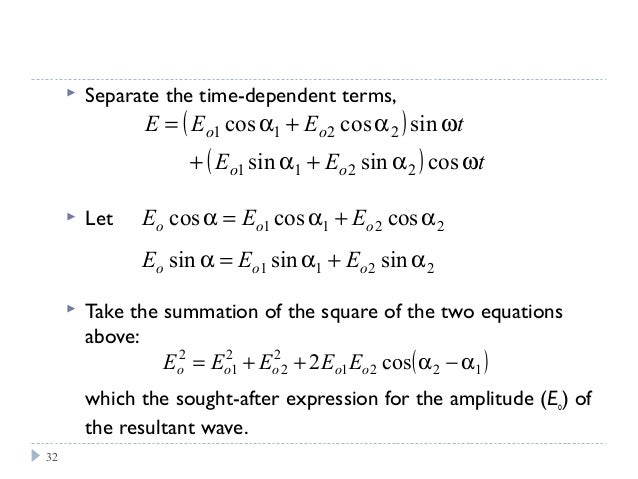
Asqrt A 11 A 22 -2A 1 A 2 cos . How do you find the resultant amplitude of three waves. The strategy consists in starting from the sought solution yres Arescost kx res and expand the cosine function yres Arescost kxcosres sint kxsinres.
Y1 y2 A1cost kx. There are two main types of interference called constructive and destructive interference. Resultant Amplitude and Intensity of Two waves in Wave Optics for JEE and NEET is the topic of this physics video lesson.
Posted on December 20 2018 Author Nicholas Idoko Categories Physics Tags calculator encyclopedia inclination angle magnitude nickzom calculator physics resultant vector vector resultant. The resultant amplitude due to superposition of two waves y1 5sin t kx and y2 5 cos t kx 150 asked Jul 10 2019 in Physics by Ritika 688k points jee. In this video we will find an expression for two waves that add together to give a resultant wave with the same amplitude as the two input waves.
Where A Resultant Amplitude a a 2aa cos ii Resultant Intensity. Two waves are represented by the equations Y1 a sint- kx and Y2 a cos t kx. All these terms are sound field quantities.
As you can see the Frequency Index looks like this. The head to tail method to calculate a resultant which involves lining up the head of.

The Resultant Amplitude Of A Vibrating Particle By The Superposition Of The Two Waves Y1 A Sin W T Pi3 And Y2 A Sinw T Is

The Resultant Amplitude Of Two Superposed Waves Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

The Resultant Amplitude Of Two Superposed Waves Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

17 Three Waves Of Equal Frequency Having Amplitude 10mm 4mm And 7mm Arrive At A Given Point With Brainly In

The Resultant Amplitude When Two Waves Of Two Waves Of Same Frequency But With Youtube

What Is The Amplitude Of Resultant Wave When Two Waves Y1 A1sin W T B1 And Y2 A2sin W T B2 Superimpose

Phase Difference Between Two Waves Having Same Frequency V And Same Amplitude A Is 2pi 3 Youtube

Question Video Identifying The Resultant Of Two Interfering Waves Nagwa

The Resultant Amplitude Of Two Superposed Waves Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Two Waves That Add To Give A Resultant With The Same Amplitude Youtube
Two Waves Have Equations Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

Resultant Amplitude And Intensity Of Two Waves In Wave Optics For Jee And Neet Youtube
The Resultant Amplitude Due To Superposition Of Three Simple Harmonic Motion X1 3 Sin Wt Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
What Is The Resultant Amplitude Of A Vibrating Particle By The Superposition Of Two Waves Math Y 1 A Sin Wt Frac P 3 Math And Math Y 2 A Sin Wt Math Quora

The Resultant Amplitude Of A Vibrating Particle By The Superposition Of The Two Waves Y1 Asin Wt P 3 Brainly In

Two Waves Having Equation S X 1 Asin Omegat Phi 1 X 2 Asin Omegat Phi 2 If In The Resultant Wave The Frequency And Amplitude Remain Equal To Those Of Superimposing Waves Then Phase Difference Between Them Is

Post a Comment for "How To Calculate Resultant Amplitude"