Resultant Amplitude Of 3 Waves
The resultant wave has an amplitude of zero. Enter the scientific value in exponent format for example if you have value as 00000012 you can enter this as 12e-6.

Oscillation And Waves Class12 Neet Mindmap Amazing Physics Notes Physics Concepts Physics Formulas
Resultant Amplitude and Intensity of Two waves in Wave Optics for JEE and NEET is the topic of this physics video lesson.

Resultant amplitude of 3 waves. Combining 1st with 3rd their resultant amplitude is given by A_12a_12a_322a_1a_3cos varphi or A_1sqrt102722xx10xx7cos pi sqrt10049-140 sqrt93mum in the direction of first. The resultant amplitude of two interfering waves is equal to the sum of those two waves displacements at the same location as the resultant wave. Then the amplitude of the resultant wave is.
Phase difference between first wave and second wave is 60. Homework Equations The Attempt at a Solution in my opinion when 2 waves superposed the resultant intensity is I1 I2 but intensity is directly proportional to amplitude square so the resultant amplitude should be. Solution For Three waves of equal frequency having amplitudes 10 mm 4 mm and 7 mm arrive at a given point with successive phase difference of 2.
The resultant amplitude of waves of equal phase and frequency is the _ asum of the squares of amplitude of individual wave bnone cDifference of amplitudes of individual waves dSum of the amplitudes of individual waves. Now combining this with 2nd wave we have the resultant amplitude A2A_12a_222A_1a_2cospi2 or Asqrt32422xx3xx4cos 90sqrt916. Please log in or register to add a comment.
If two identical waves are traveling in the same direction with the same frequency wavelength and amplitude. The resultant amplitude due to superposition of three simple harmonic motion x1 3 sin t The resultant amplitude due to superposition of three simple harmonic motion x1 3 sin t x2 5 sin t 37 and x3 -15 cos t is. Calculate the ratio of maximum and minimum intensities of the resultant wave.
Each wave is a periodic disturbance. Find resultant intensity at this point. Resultant wave is A1 A2 2A.
The wave 1 and 3 reach out of phase. Intensity corresponding to A_0 is I_0. They will interfere to create a trough with an amplitude of 6.
Given a problem of this nature this is what I would think of doing. T0 we get A_ res cos0 A_1cos0 A_2cos0- phi implies A_ res A_1 A_2cosphi. Hence it is the required solution.
They are superimposed on each other. At is the Amplitude of Resultant Reflected Waves k1 is the For Wave 1 k2 is the For Wave 2 A is the Amplitude Instructions to use calculator. Resultant amplitude of each is A_0.
Resultant amplitude of 1 and 3 107 3 m This wave has phase difference of 2 with 4 m Resultant amplitude 32425m. We get Therefore a new wave will form of resultant amplitude of 6. Three waves from three coherent sources meet at some point.
Why the ans shouldnt be sum of amplitude. How do you find the resultant amplitude of three waves. Amplitude is the maximum displacement of the wave.
Interactions between two interfering waves Resultant amplitude Displacement Constructively interfering waves Destructively interfering waves Skills Practiced. In this case A3 and. We know resultant amplitude of two waves of same amplitude A with phase difference is given by.
BUT differ in phase the waves add together. Please use the mathematical deterministic number in field to perform the calculation for example if you entered x greater than 1. The displacement y2 and y3 have a phase difference of 3 3.
Hence resultant phase difference between them is. Determine the amplitude of the resultant wave when two sinusoidal waves having the same frequency and traveling in the same direction are combined if their amplitudes are 30 cm and 40 cm and they differ in phase by texpi2tex rad Homework Equations yxtasinkx-wt yxtbsinkx-wttexphitex texphitex phase difference. The first wave lags behind in phase angle from second and third wave.
Two waves of equal frequencies have their amplitudes in the ratio of 3. Allsm 11 5 months ago. Note that y1 and y4 are out of phase and interfere destructively.
They are superimposed on each other. The amplitude of the resulting wave in mm is given by. Given this information how can we find the amplitude of the resultant wave.
Yxt y_1xt y_2x t A_ rescoskx-omega t A_1coskx-omega t A_2coskx-omega t -phi textSetting x0. Putting value of A and in above equation. Path difference between first wave and third wave is lambda3.
Any other phase difference results in a wave with the same wave. When 0 crest to crest and trough to trough then cos 2 1. When the two waves have a phase difference of zero the waves are in phase and the resultant wave has the same wave number and angular frequency and an amplitude equal to twice the individual amplitudes part a.
Three coherent waves having amplitudes 12 mm 6 mm and 4 mm arrive at a given point with successive phase difference of 2. If the phase difference is latex 180text latex the waves interfere in destructive interference part c. The amplitude of the resultant wave is Ar3A A r 3 A and its intensity is IrcA2r3cA23I0 I r c A r 2 3 c A 2 3 I 0.
This is constructive interference.

Wave Interference Venn Diagram Venn Diagram Diagram Waves
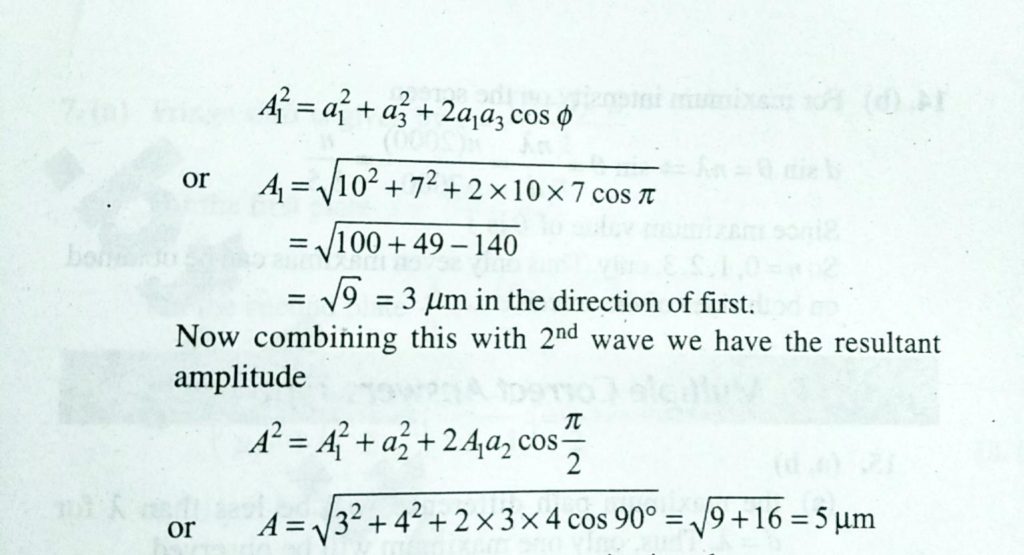
Three Waves Of Equal Frequency Having Amplitudes 10 Mm 4mu M 7 Mm Arrive At A Given Point With Successive Phase Difference Of P 2 The Amplitude Of The Resulting Wave In Mm

Chapter 14 Superposition And Standing Waves Waves Vs
Three Waves Of Equal Frequency Having Amplitudes 10 Mm 4 Mm And 7 Mm Arrive At A Given Point With Successive Phase Difference Of P 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

Three Waves From Three Coherent Sources Meet At Some Point Resultant Amplitude Of Each Is A 0 Youtube

Find The Resultant Amplitude And The Phase Difference Between The Resultant Wave And The First W Youtube

Three Waves Y 1 2 A Sin W T Pi3 Y 2 2 A Sin W T Pi3 And Y 3 A Sin W T Interfere Each Other The Amplitude Of The Resultant Wave Is
Resultant Amplitude And Intensity Myrank

Three Sound Waves Of Equal Amplitudes Have Frequencies V 1 V V 1 They Superpose Youtube

Concept Map Of Wave Motion For Quick Understanding Of Physics Physics Concepts Physics Topics Physics
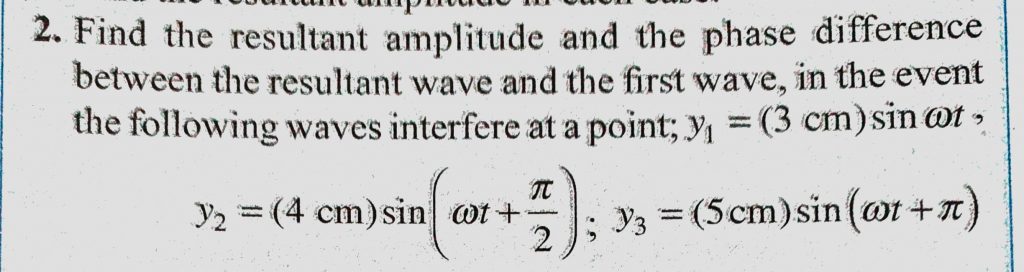
Find The Resultant Amplitude And The Phase Difference Between The Resultant Wave And The First Wave In The Event The Following Waves Interfere At A Point Y1 3 Cm Sin Omega

Three Waves Of Equal Frequency Having Amplitudes 10mum 4mum 7mum Arrive At A Given Point With Successive Phase Difference Of Pi 2 The Amplitude Of The Resulting Wave In Mum Is Given By

Waves Review Practice Worksheet Practices Worksheets Worksheets Algebra Worksheets

16 5 Interference Of Waves University Physics Volume 1

Three Waves Of Equal Frequency Having Amplitude 10mm 4mm And 7mm Arrive At A Given Point With Successive Phase Difference Is Pie 2 The Amplitude Of The Resulting Wave In Mm Is Given By

Quick Revision General Waves Properties Physics And Mathematics Basic Concepts Physics Concepts
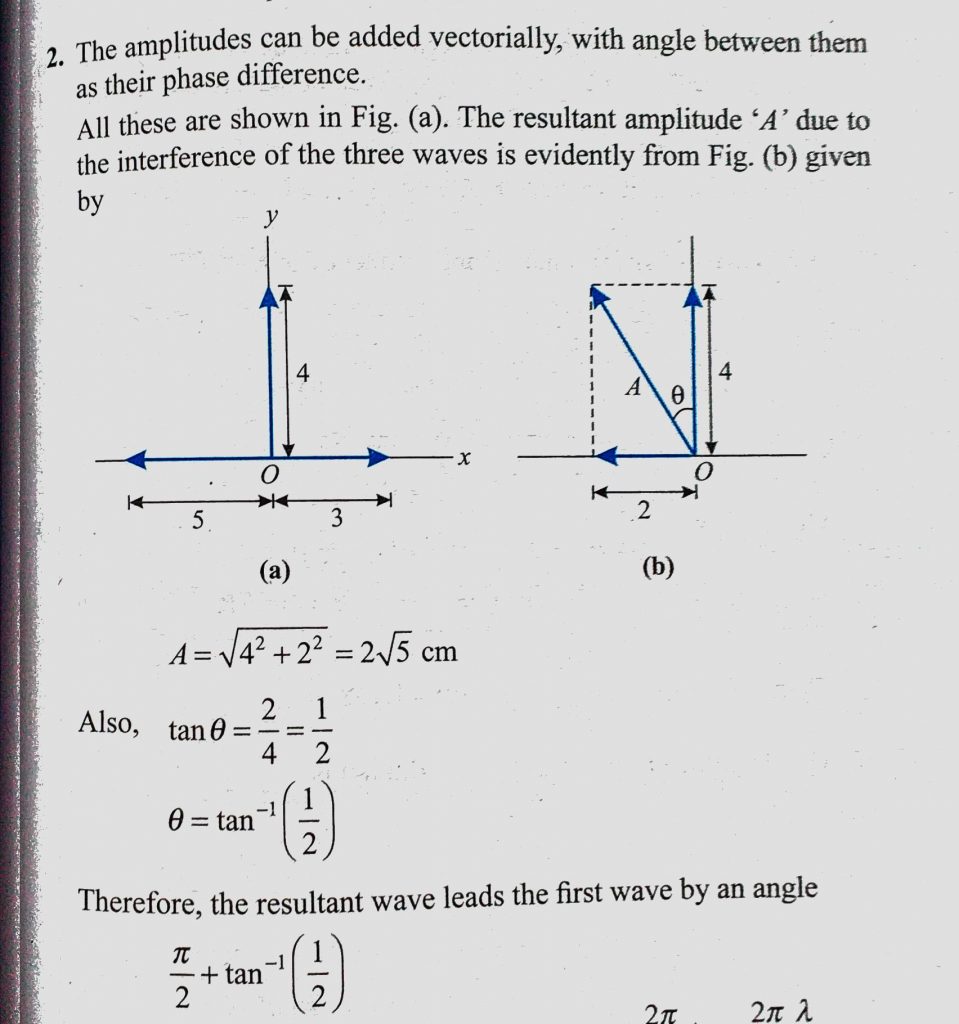
Find The Resultant Amplitude And The Phase Difference Between The Resultant Wave And The First Wave In The Event The Following Waves Interfere At A Point Y1 3 Cm Sin Omega

Three Waves From Three Coherent Sources Meet At Some Point Resultant Amplitude Of Each Is A 0 Intensity Corresponding To A 0 Is I 0 Phase Difference Between First Wave And Second Wave Is 60

Post a Comment for "Resultant Amplitude Of 3 Waves"